Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, providing a highly precise and efficient method for producing a wide array of components. In this article, we’ll understand the comprehensive process of CNC machining, highlighting each stage involved in transforming digital designs into tangible, intricately crafted products.
Design and Programming:
The process begins with the creation of a detailed digital design using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This design serves as the blueprint for the desired part or component. Subsequently, the CAD file is translated into a CNC-compatible program using Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. This program contains the instructions that will guide the CNC machine in executing the necessary cuts and operations.
Material Selection and Workpiece Setup:
Once the first step is done, the appropriate raw material is selected. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the final product. The raw material is then securely fixed to the CNC machine’s worktable, ensuring stability during the machining process. Proper workpiece setup is crucial for achieving accuracy and precision in the final output.
Tool Selection:
CNC machining involves the use of various cutting tools, each designed for specific tasks. The selection of tools depends on factors such as material type, desired surface finish, and the intricacy of the design. Tools range from end mills for general cutting to specialized tools for contouring and finishing. The CNC program dictates the sequence of tool changes and the specific operations each tool will perform.
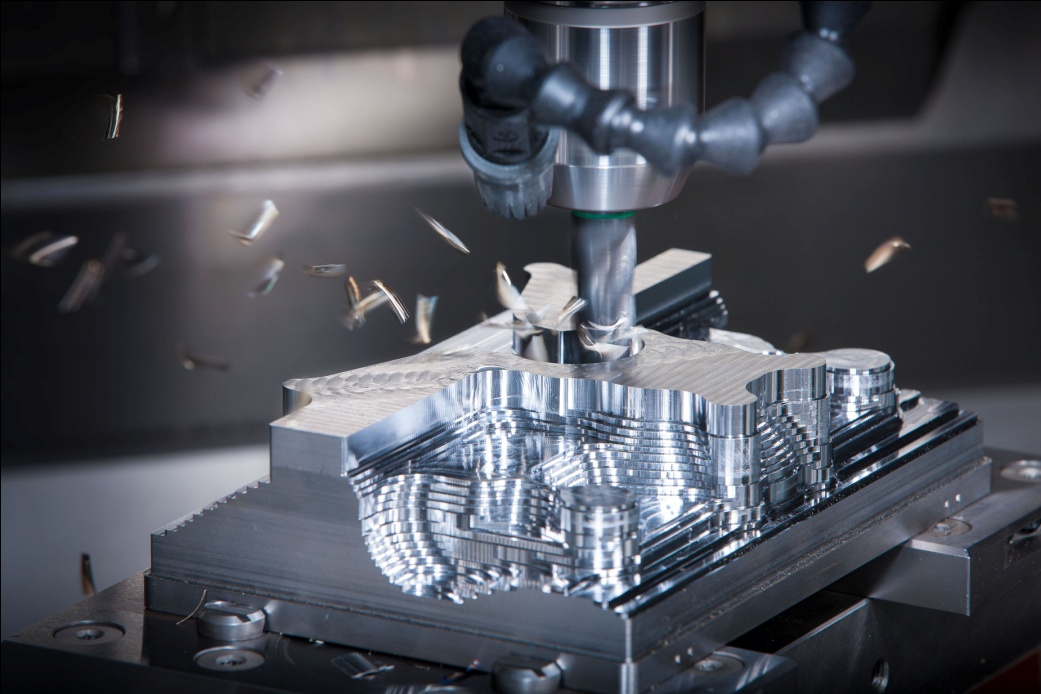
Machining Operations:
Based on the programmed instructions, the CNC machine executes a series of machining operations. These operations include milling, turning, drilling, and other cutting processes. During milling, for example, the rotating cutting tool removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape. The precision and repeatability of CNC machining ensure consistency across multiple parts.
Quality Control:
Quality control is an integral part of the CNC machining process. Throughout production, operators monitor the machining parameters and inspect the workpiece for accuracy and surface finish. Any deviations from the specifications can be adjusted in real-time, ensuring that the final product meets the required standards.
Post-Processing:
Once the machining operations are complete, post-processing steps may be necessary. This can involve additional treatments such as heat treatment, coating, or surface finishing to enhance the physical and aesthetic properties of the component.
In this way, your digital design becomes a tangible reality. And, with Locus Precision, you are assured the best results.